- demo@example.com
- Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur.

Vaginal tightening is a specialized procedure that focuses on restoring the firmness, tone, and elasticity of the vaginal area. It is commonly chosen by women who experience vaginal laxity due to childbirth, aging, or hormonal changes. Depending on individual needs, both non-surgical and surgical options are available.
Non-surgical vaginal tightening treatments are minimally invasive and require no cuts, stitches, or anesthesia. These procedures use advanced technologies to stimulate natural collagen production and rejuvenate vaginal tissues.
Common non-surgical methods include:
• Laser Therapy (CO2 or Er:YAG): Improves tightness, lubrication, and tissue elasticity.
• Radiofrequency (RF) Treatment: Uses gentle heat to stimulate collagen and tighten internal tissues.
• Ultrasound-Based Therapy: Delivers focused energy to deeper layers for tissue remodeling.

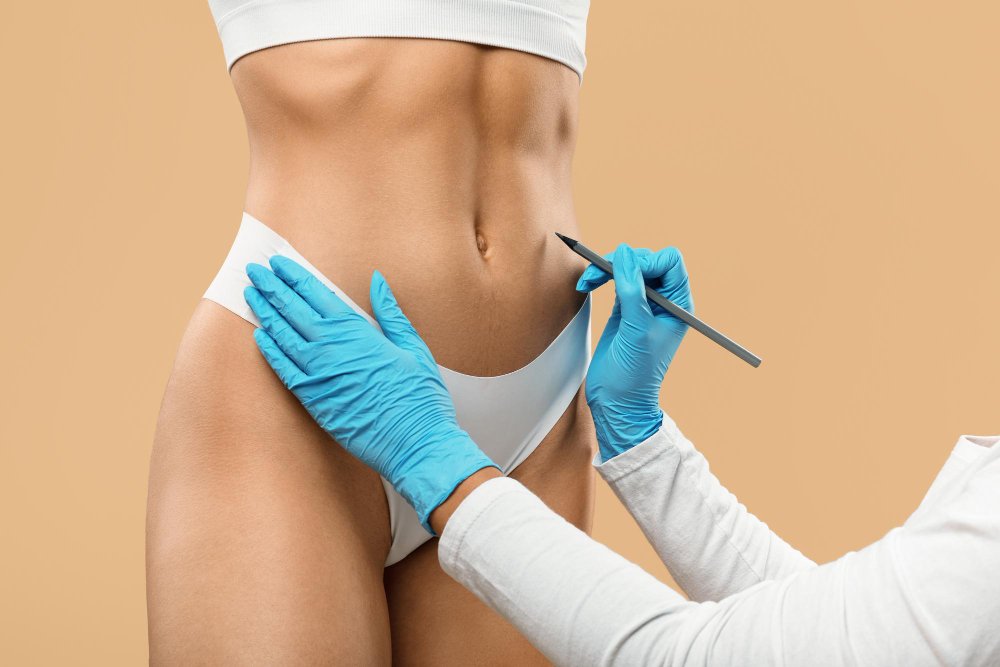
Surgical vaginal tightening is a more comprehensive option designed for women with moderate to severe vaginal laxity. This procedure involves tightening the vaginal muscles and removing excess tissue to restore the vaginal canal’s structure and tone.
Performed under anesthesia, surgical tightening is also referred to as vaginoplasty or perineoplasty, depending on the area addressed. It offers more dramatic and long-lasting results but requires a longer recovery period—typically 4 to 6 weeks. During this time, physical activity and sexual intercourse should be avoided to ensure proper healing.
Surgical vaginal tightening is ideal for women seeking significant improvement in vaginal tone, often after multiple childbirths or with advanced age-related changes.
Both approaches offer unique benefits. Non-surgical treatments provide a quick, low-risk option with no downtime, while surgical procedures offer permanent structural improvement for more pronounced concerns. A consultation with a qualified professional is the best way to determine which method is right for you.